
Basic HR Learning method is on the way is now easy. The fast-moving Human Resources field demands that vital metrics be kept under close watch to maintain a fruitful and effective workforce. Knowing what these metrics mean and, even more importantly, what they indicate when they change helps HR departments make better decisions, improve conditions for employees, and drive the organization toward its goals. Here are ten HR metrics that every HR pro should keep an eye on.
1. Turnover Rate
The turnover rate measures the percentage of employees who leave an organization over a specific period. High turnover can indicate underlying issues such as job dissatisfaction, poor management, or inadequate compensation. Monitoring this metric helps HR identify trends and implement strategies to improve employee retention.
Formula:
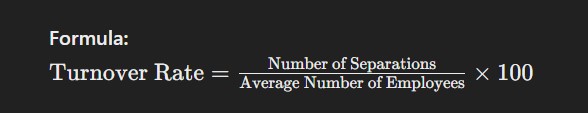
2. Cost Per Hire
Cost per hire is the total expense incurred in hiring a new employee, including advertising, recruitment agency fees, relocation expenses, and training. This metric is essential for budgeting and assessing the efficiency of the hiring process.
Formula:
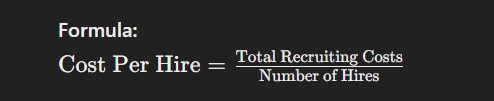
3. Time to Fill
Time to fill measures the number of days it takes to fill a vacant position, from the initial job posting to the candidate’s acceptance of the offer. A shorter time to fill indicates an efficient recruitment process, while a longer time may suggest challenges in finding the right talent.
Formula:

4. Training Cost Per Employee
This metric calculates the average amount spent on training each employee. It includes costs associated with training programs, materials, trainers’ fees, and lost productivity during training sessions. Understanding this metric helps HR optimize training budgets and improve the effectiveness of development programs.
Formula:
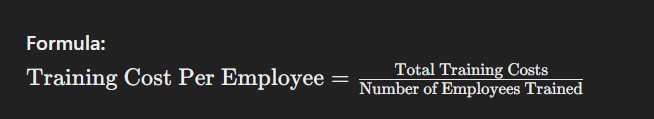
5. Absenteeism Rate
The absenteeism rate tracks the percentage of workdays missed by employees due to unplanned absences. High absenteeism can disrupt productivity and may indicate issues such as poor workplace morale or health problems.
Formula:

6. Employee Engagement Score
Employee engagement score reflects the level of commitment and enthusiasm employees have towards their work and the organization. High engagement typically leads to better performance, higher retention rates, and overall job satisfaction. Regular surveys and feedback mechanisms can help HR measure and improve this score.
7. Offer Acceptance Rate
This metric measures the percentage of job offers accepted by candidates. A low offer acceptance rate might indicate issues with the compensation package, job role, or company reputation. Monitoring this metric helps HR refine their recruitment strategies.
Formula:
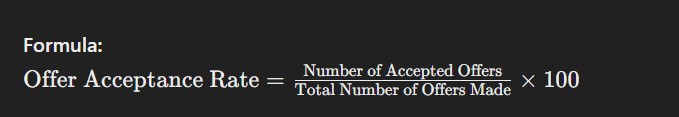
8. Revenue Per Employee
Revenue per employee is a productivity metric that shows how much revenue each employee generates. It helps HR assess the efficiency of the workforce and its contribution to the company’s profitability.
Formula:
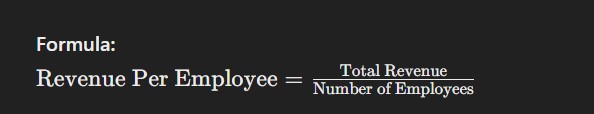
9. Salary Increase Rate
The salary increase rate measures the percentage increase in employee salaries over a specific period. This metric is important for ensuring competitive compensation practices and managing payroll budgets effectively.
Formula:
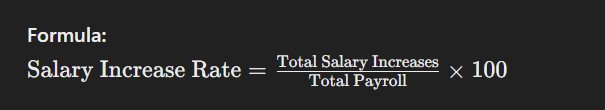
10. Employee Productivity Rate
Employee productivity rate evaluates the output of employees relative to the input, such as time or resources. This metric is key to understanding how efficiently employees are performing their tasks and how well they contribute to organizational goals.
Formula:
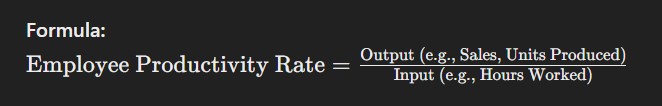
Conclusion
These key measures in the HR domain let us peek not just into the current state of affairs in an organization but also into its future. When we take a look at the present and project to the future, we see stuff—workforce stuff, to be more precise. And it isn’t just any kind of stuff. It’s the engaged, productive, and satisfied stuff in the employees’ right and happy space. That is, if the stuff is engaged, productive, satisfied, and right, it is also propelling the organization to its goals, which makes it right and makes us all winners.



